Zero Trust Security Architecture
Zero Trust Security Architecture is a cybersecurity model that assumes no user or device is inherently trusted, requiring continuous verification, strict access controls, and micro-segmentation to protect networks and data.
What is Zero Trust Security and Why You Should Adopt It
Understanding Zero Trust Security
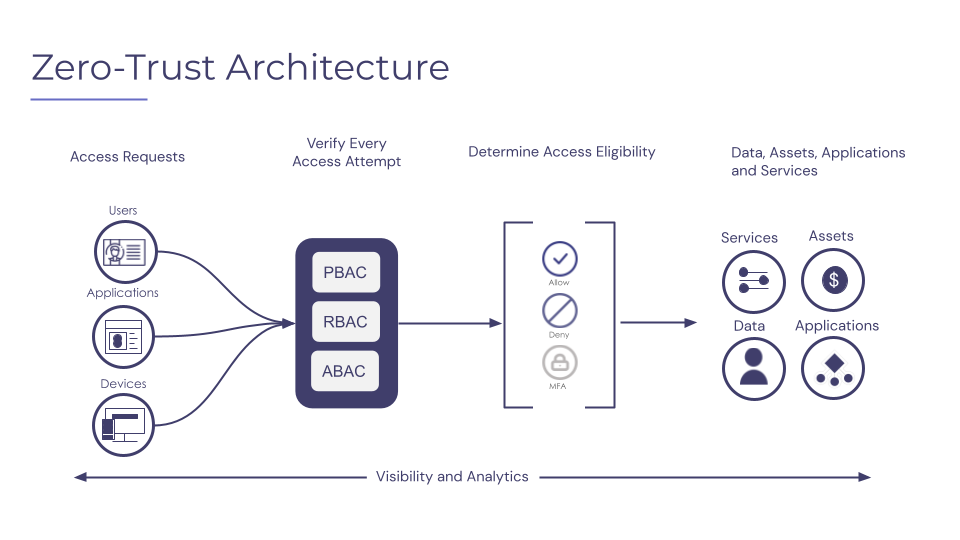
Zero Trust Security is a cybersecurity model that operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify.” Unlike traditional security models that assume entities inside a network are trustworthy, Zero Trust requires continuous authentication and authorization of every user, device, and system attempting to access resources. It minimizes risk by enforcing strict identity verification and limiting access to only what is necessary.
Key Principles of Zero Trust
- Verify Identity and Access – Every access request must be authenticated, authorized, and continuously validated before granting entry.
- Least Privilege Access – Users and devices should have only the minimal access necessary to perform their functions.
- Microsegmentation – Networks are divided into smaller zones to limit lateral movement and contain potential threats.
- Assume Breach Mentality – Organizations operate under the assumption that breaches have already occurred, continuously monitoring for unusual behavior.
- Continuous Monitoring and Logging – Real-time analysis of access patterns, user behavior, and system interactions ensures rapid threat detection and response.
Why Businesses Should Adopt Zero Trust Security
1. Enhanced Security Posture
By removing implicit trust and enforcing strict authentication, Zero Trust significantly reduces the risk of cyberattacks, insider threats, and data breaches.
2. Protection Against Modern Cyber Threats
With cybercriminals employing increasingly sophisticated attack methods, Zero Trust ensures that even if an attacker gains access, they cannot move freely within the network.
3. Improved Regulatory Compliance
Zero Trust aligns with industry standards and regulatory frameworks such as GDPR, HIPAA, and NIST, making compliance easier for businesses.
4. Reduced Attack Surface
Microsegmentation and strict access controls prevent attackers from easily navigating an organization’s network.
5. Better Visibility and Control
With continuous monitoring and real-time logging, security teams gain deeper insights into network activity, enabling proactive threat management.
How to Implement Zero Trust Security
- Identify and Classify Assets – Determine all critical assets, including applications, data, and devices.
- Enforce Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM) – Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC).
- Segment the Network – Use microsegmentation to create secure perimeters around sensitive data.
- Monitor and Analyze Activity – Deploy security analytics tools to detect anomalies and respond to threats promptly.
- Adopt a Continuous Improvement Approach – Regularly update security policies, test defenses, and adapt to emerging threats.
Conclusion
Zero Trust Security is a proactive approach to cybersecurity that offers robust protection against evolving cyber threats. By enforcing strict access controls, continuous monitoring, and an assume-breach mentality, businesses can significantly enhance their security posture, minimize risks, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. Adopting a Zero Trust model is no longer an option but a necessity in today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape.